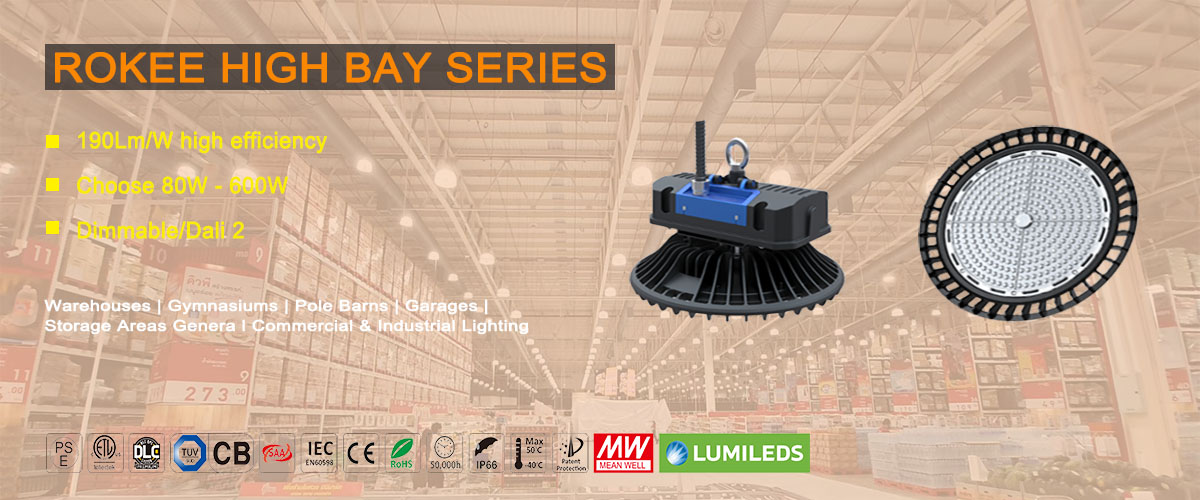
LED High Bay Light Selection Guide
For decades, high bay lighting has been a popular choice for commercial and industrial users around the world because of its relatively compact size and strong lumen output. Over the past few years, LED technology has come to dominate the high bay lighting market because of its improved energy efficiency and longevity, as well as greatly improved colour rendering accuracy. This major leap in high bay lighting technology has resulted in significant operational and maintenance cost savings for users, as well as improved workplace safety and efficiency.
Definition
High Bay Lights - This is a special class of lighting fixtures designed to be mounted in high locations to provide vertical space for daily operations and to provide a wide range of lighting capabilities. High bay lights have a high lumen output and are suitable for industrial and commercial environments.
Lumens- This is the unit of measurement for the amount of visible light emitted by a light source. In the past, light output was often quantified in watts rather than lumens. This is because there is a linear relationship between the wattage and lumen output of traditional incandescent lamps. Because the lumen output of LED lighting is so different than traditional lighting sources, it is now standard to compare light based on lumen output.
Colour Temperature - Colour temperature is used to define the hue of a light and is measured in Kelvins, ranging from 1,000K to 10,000 K. The most common colour temperatures used in commercial lighting today are in the range of 3000K to 6500K, with 5000K being the closest to daylight.
Colour Rendering Index - Also commonly abbreviated as ‘CRI’, this is a scale of measurement used to determine the accuracy of a light and its correct colour rendering properties. The value ranges from zero all the way up to 100, with 100 being the CRI of daylight, which is considered a perfect light source. The higher the CRI of a light, the more accurately it illuminates its surroundings.
Choosing the Wattage of LED High Bay Lights
High bay lights come in a variety of wattages to suit various applications and lighting requirements. In the past, the output of the lights was usually measured in watts, as performance was very consistent across different manufacturers for a given wattage range. This made it easy for buyers to select replacement lamps, as well as plan the number and placement of lamps in new construction.
However, in today's market, performance varies widely from manufacturer to manufacturer, with some offering much more efficient lighting than others.The much lower wattage required for LED lamps compared to traditional lighting also makes it difficult for those familiar with metal halide and HID technology to select the correct wattage of LED high bay lamps for their application. The table below highlights the common HID wattage ranges for high bay lights and how they correspond to modern LED technology to aid in the selection process.
Low wattage (80-100 watts) - The wattage of these lamps is generally between 80 and 1500 watts. They are most popular with users who want to illuminate smaller areas in the most energy efficient way. Most high shed lights in this wattage range also have the advantage of being able to plug into an existing outlet and be used without manual rewiring.
Medium wattage (150-300 watts) - Medium wattage high shed lamps are currently the most popular lamps for commercial and industrial users. Lamps in this wattage range provide the best balance of lumen output and power consumption for most applications and are commonly found in warehouses, commercial facilities and manufacturing centers.
High power watage (400-600 watts) - At the top end of the wattage range, these lights provide the most intense lighting while still having the energy saving benefits of LED technology. It is most commonly used in sports venues, stadiums, and other high-ceiling facilities that require a lot of light.
Appropriate lumen level
Choosing the right lumen grade for your application is critical to getting the right lighting performance and ensuring maximum return on investment. In fact, in today's market, lumen output has replaced wattage as the main indicator of lighting performance. Considering that most people still think of lighting performance in terms of wattage, converting lumens into the primary measure of lighting output can be a confusing task. However, this is how the lighting industry will measure performance for the foreseeable future, so understanding how lumen grades translate to real-world performance is critical.
In LED lighting, the number of lumens produced is usually proportional to the wattage of the fixture, although this depends on the manufacturer. Therefore, we have listed several common lumen ranges to help simplify the buying process:
Low lumen (11,200-14,000) - Low lumen range, these lamps are primarily used in applications that require high value light and have excellent energy efficiency. These lamps are typically used to illuminate small to medium area areas in manufacturing and commercial facilities, or non-critical areas where bright light is not required.
Medium lumen (21,000-42,000) - This is currently the most popular lumen range, and such lights are typically used in large venues such as warehouses and large commercial facilities. They are highly sought after for their outstanding lighting capabilities and balance of energy efficiency. In addition, these lights are usually moderately priced and therefore available to a wide range of users.
High lumen (56,000-84,000) - This class of lights is by far the most powerful and is used for situations where maximum illumination is the main goal. While these lights still have the energy saving benefits of LED technology, they consume the highest wattages of all high-shed lights to provide lumen output. These lights are commonly used in stadiums, arenas, public Spaces, and other areas that require accurate and intense lighting.
Color Temperature
In addition to choosing the right wattage and lumen output for your application, it is also important to determine the correct color temperature. This will depend on the overall purpose and objective of the lighting. Certain color temperatures are more conducive to ensuring workers' attention and productivity, while others are more conducive to relaxation and positive emotions. Below we have summarized the most common color temperatures in high shed lighting today to assist in the buying process.
5000K-5000 Kelvin LED high shed lights are the most common at present. This color temperature projects cool white lighting that simulates daytime conditions. This is ideal for general lighting in warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and other commercial Spaces that require precise lighting. This color temperature is also best for high CRI lighting, as it is the most natural of all color temperatures.
4000K-4000 Kelvin LED bulbs project natural colors common in the workplace. While these bulbs are generally less common than 5000K high-shed fixtures, there are still many electrical contractors and building managers who prefer this color temperature. This is because it feels warmer and is very similar to the color temperature of traditional lighting such as HID and fluorescent lamps. Therefore, 4000K high ceiling lights can be seen everywhere in the entire LED lighting market.
3000K - 3000 Kelvin is a warm color LED light, mainly used in restaurants or houses. 3000K LED bulbs are rarely seen in high-shed lighting because these lights are designed for large buildings (such as warehouses and commercial gyms), not residential or hotel lighting applications.
Application and Type
High Bay lights are used in a wide variety of commercial and industrial applications, including workshops, automotive repair shops, warehouses, manufacturing plants, fitness centers, indoor sports arenas, and even large retail stores. Their high power dimension ratio makes them ideal for applications where traditional lighting cannot provide adequate illumination.
The following is a list of the most common types of high bay lighting fixtures:
UFO High Bay Light- Named for their resemblance to the quintessential UFO, these round fixtures are a staple lighting choice for warehouses, workshops and other industrial areas. They are popular due to several key factors that make them an excellent choice, including superior durability, high lumen output, and a compact design that is easy to set up and install. This design provides highly focused lighting while maintaining high energy efficiency and low maintenance costs.

Linear High Bay Lights - These long LED fixtures are popular in applications that require high bay lighting that is dispersed over a wider area than regular UFO lights. Linear highbay fixtures are popular in commercial facilities and warehouse areas, especially those that value simplicity and cost-effectiveness in facility lighting setups. They offer a wider beam angle than UFO-style highbay fixtures, allowing them to illuminate a larger area with lower lumen intensity.

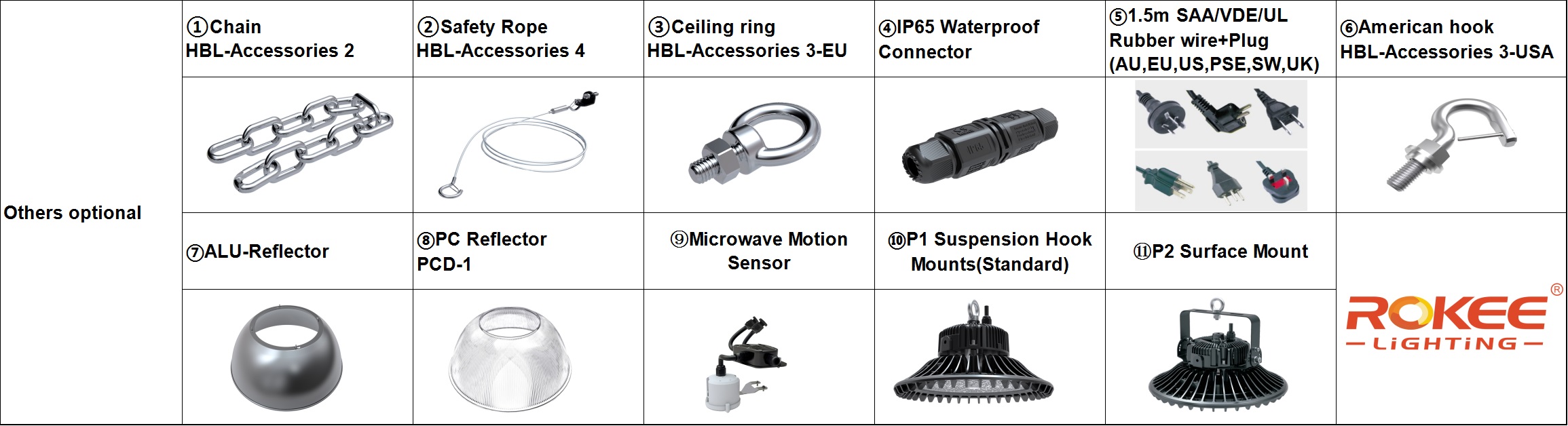
Mounting Options
Suspension Ring Mounts- By far the most popular of all high bay mounting systems, these mounts allow the lights to be suspended from the ceiling at variable distances depending on the application. While these mounts require some degree of customization to the suspension system, they are relatively simple to install and sometimes do not require any modifications to the mounting points. They usually use cables or chains for the suspension system, but they can technically be mounted anywhere with hooks.
Surface Mount - For applications that require maximum vertical clearance under the luminaire, surface mount is the closest fit. To accomplish this, surface mount fixtures feature low-profile fixed angle brackets that allow the fixture to be placed as close as possible to the ceiling or mounting surface while still providing enough clearance for heat and ventilation.
Pole Mount- Similar to suspended mounting, this mounting system uses conduit style rods to attach the high bay fixture to a metal mounting plate secured to the ceiling. This is the sleekest of all suspended mounting systems because it allows the wires to be encased in smooth rods that can then be painted or designed to fit inside the facility.